As more individuals explore alternatives to conventional gasoline-powered cars, electric units (EVs) are growing in popularity. When we talk about components of electric vehicles, EVs’ advantages in terms of the environment, since they release much fewer greenhouse gases than their gasoline-powered equivalents, are one of the primary factors influencing this transition. With particular components of electric vehicles that enable them to run on electricity, an electric vehicle’s design and functioning are distinct from those of a conventional gasoline-powered automobile.
“Components of an electric vehicle” refers to the many elements and systems that work together to power and manage the vehicle’s mobility. Understanding the parts of an electric car is crucial for comprehending how these vehicles operate and how they vary from conventional automobiles. Everything from the battery pack and electric motor to the power electronics and charging system is included in this category.
Parts For An Electric Car
The intricate parts of an electric vehicle are essential to supplying the car with electricity and regulating its motion.
Battery pack
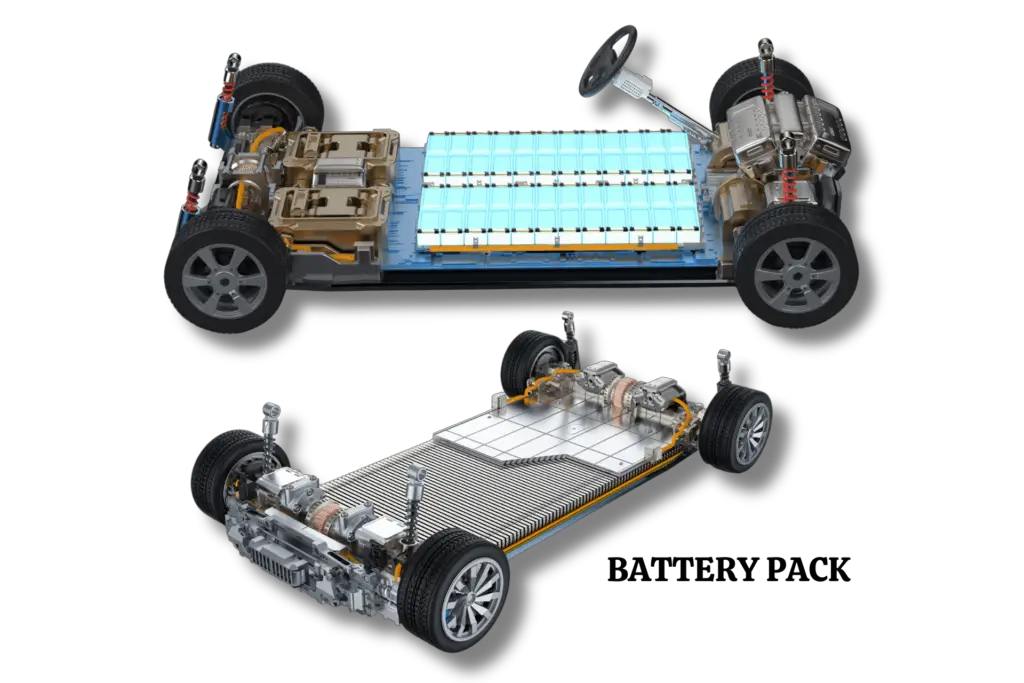

The battery pack, one of the most important components of an electric car, stores the energy necessary to power the electric motor. Because of recent advancements in battery technology that allows for the storage of more energy in a given volume, the range of electric cars has grown.
Various batteries may be used in an EV, but lithium-ion batteries are the most well-known due to their high energy density and extended lifespan.
The battery pack is often positioned beneath the vehicle’s floor, which reduces the centre of gravity, enhances handling, and makes the most of the interior space. Several manufacturers are looking into innovative materials and designs to decrease weight and improve efficiency because the battery pack contributes significantly to the car’s overall weight.
Electric motor
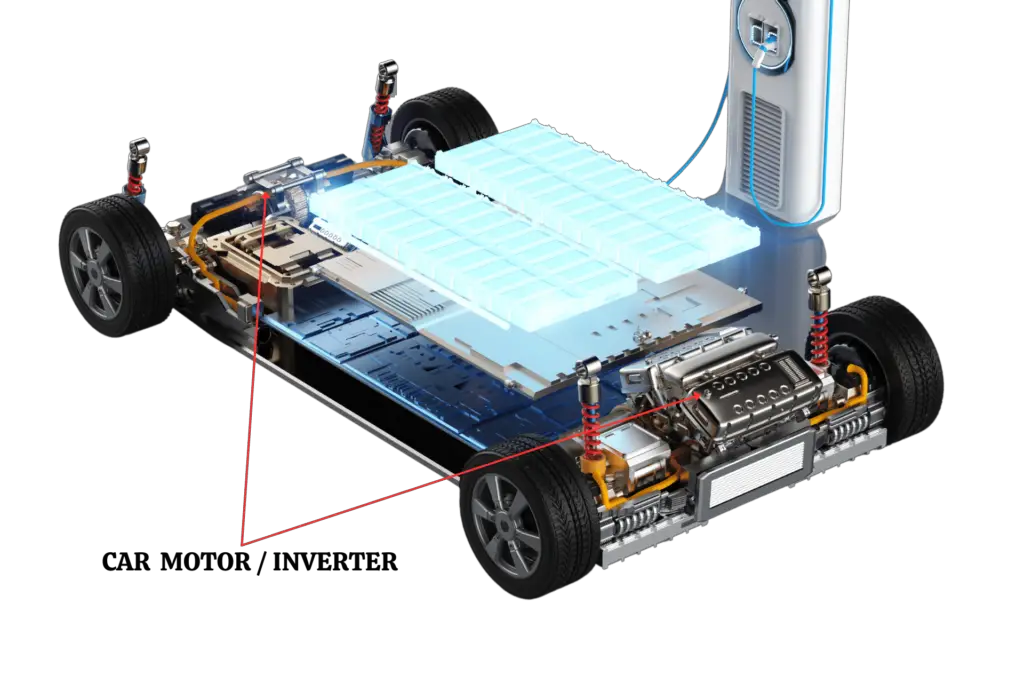
The electric motor is a critical component of an electric automobile since it converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to power the vehicle. An electric motor produces rotational force using a magnetic field instead of an internal combustion engine, which requires fuel.
The electric motors found in EVs come in various designs, each with unique benefits and drawbacks, such as AC induction motors and permanent magnet motors.
Since they can turn up to 90% of the energy they receive into mechanical energy, electric motors are more efficient than gasoline engines. This is one of their main benefits.
Gas engines only convert around 30% of the energy they get into mechanical energy. Furthermore, compared to internal combustion engines, electric motors are substantially simpler and require less maintenance, which can help minimize the overall cost of ownership during the vehicle’s life.
Power Electronics

Power electronics are an important component of an electric vehicle’s powertrain because they control the energy flow between the battery, electric motor, and other components within the vehicle.
The power electronics system, which comprises an inverter, converter, and DC-DC converter, transforms the direct current (DC) power from the battery into alternating current (AC) power for the motor and other components in the vehicle.
The converter turns three-phase AC power from the battery into DC power for equipment such as the air conditioner and the car’s onboard computer. At the same time, the inverter converts DC electricity from the battery into three-phase AC power.
The DC-DC converter reduces the voltage of the high-voltage battery to low-voltage power equipment such as lights and radios. Being able to regulate the flow of electricity precisely can assist in increasing range and reducing energy consumption, making power electronics essential to the effective operation of an electric vehicle.
Onboard charger
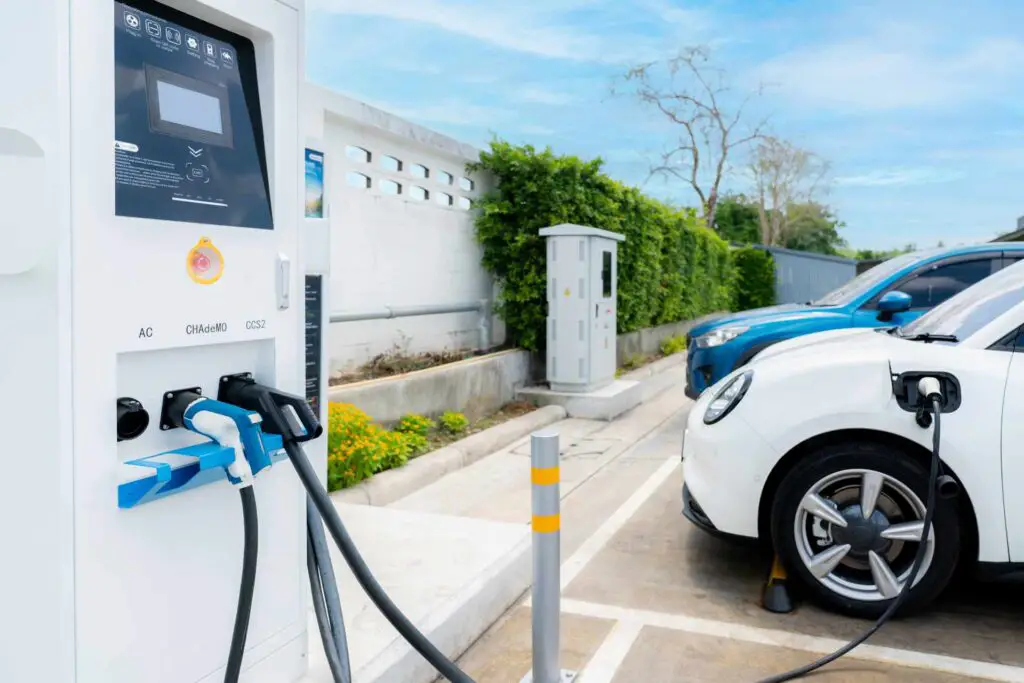

The onboard charger is an essential component of an electric vehicle because it transforms alternating current (AC) power from a charging station into direct (DC) current that may be stored in the battery.
Depending on the kind of charging station used, the onboard charger can be AC or DC and is usually found within the car. DC charging is quicker but calls for specialist charging equipment, whereas AC charging is slower but more readily accessible. With sophisticated management systems that monitor the charging process and change the power output as necessary, the onboard charger is made to be dependable and efficient.
Several contemporary EVs include cutting-edge technologies, such as wireless and quick charging, which can increase their comfort and usefulness.
The onboard charger, in general, is a crucial element that makes it possible for electric vehicles to be charged fast and effectively, giving them a competitive option to conventional gasoline-powered automobiles.
Regenerative braking system

Regenerative braking is a cutting-edge feature of electric cars that recovers energy lost during braking to recharge the battery.
When you use the brakes on an electric vehicle, the electric motor reverses, transforming the car’s kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This helps increase the vehicle’s range while restricting the wear and tear on the braking rotors and pads.
Regenerative braking is very useful in stop-and-go traffic since it may produce a lot of energy when you brake often. From the battery pack and electric motor to the power electronics and charging system, these components are all included.
DC-DC converter
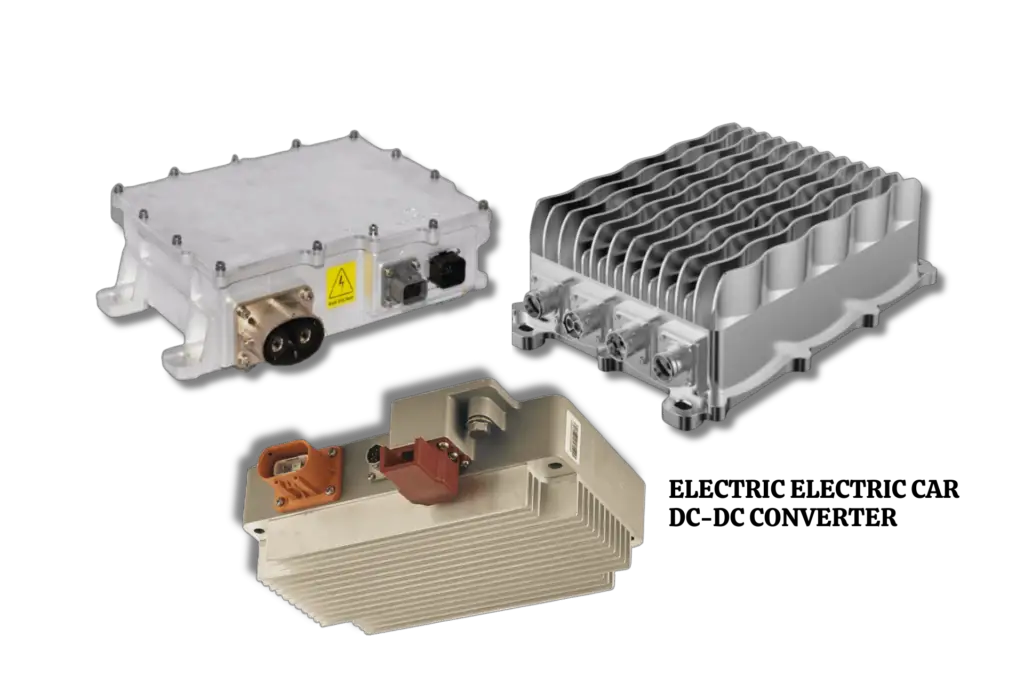
The DC-DC converter is a critical component of an electric vehicle because it transforms the high-voltage DC electricity from the battery into the lower-voltage DC power required to run the car’s onboard electronics, such as the lights, radio, and air conditioning.
The converter is designed to be dependable and efficient, with complex control systems that can vary the output voltage as needed. It is often installed between the battery and the low-voltage system.
Also, the DC-DC converter is made to be lightweight and small, which aids in making the electrical system of the car lighter and smaller. The converter is a crucial part that ensures the onboard electronics of the automobile operate dependably. By working efficiently, the converter may increase the vehicle’s range by reducing energy usage.
Thermal management system
The thermal management system, which regulates the temperature of the battery and other key components, is a crucial component of an electric vehicle.
During operation, electric cars produce a large amount of heat, which can result in decreased efficiency and quicker battery and other system wear and tear. The thermal management system’s insulation, heating, cooling, and other components keep the temperature steady. The battery and other components produce surplus heat, which the cooling and heating systems are intended to remove.
In cold weather, the heating system aids in warming the battery. By keeping the battery from becoming too hard, which can also lower performance, the insulation aids in heat retention. An electric vehicle’s heat management system is crucial to its dependable functioning, and it may assist in increasing the battery’s and other vital components’ lifespans by operating efficiently. The thermal management system, in general, is a crucial part that enables electric cars to run safely and dependably in various climatic circumstances.
Transmission or Direct Drive
Electric cars lack a typical transmission mechanism, unlike conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. Instead, they usually use a single-speed gearbox system or a direct drive. There is no need for a gearbox with natural drive systems since the electric motor is connected directly to the wheels.
The Drive and torque of the electric motor are adjusted using a fixed-ratio gearbox in single-speed transmission systems. An electric car’s transmission system is made to be lightweight, practical, and lose as little energy as possible via friction. In addition to lowering maintenance needs, this helps to enhance the vehicle’s efficiency and range. The lack of a traditional gearbox system helps simplifies the vehicle’s drivetrain, improving reliability and making maintenance easier.
The vehicle control unit (VCU)
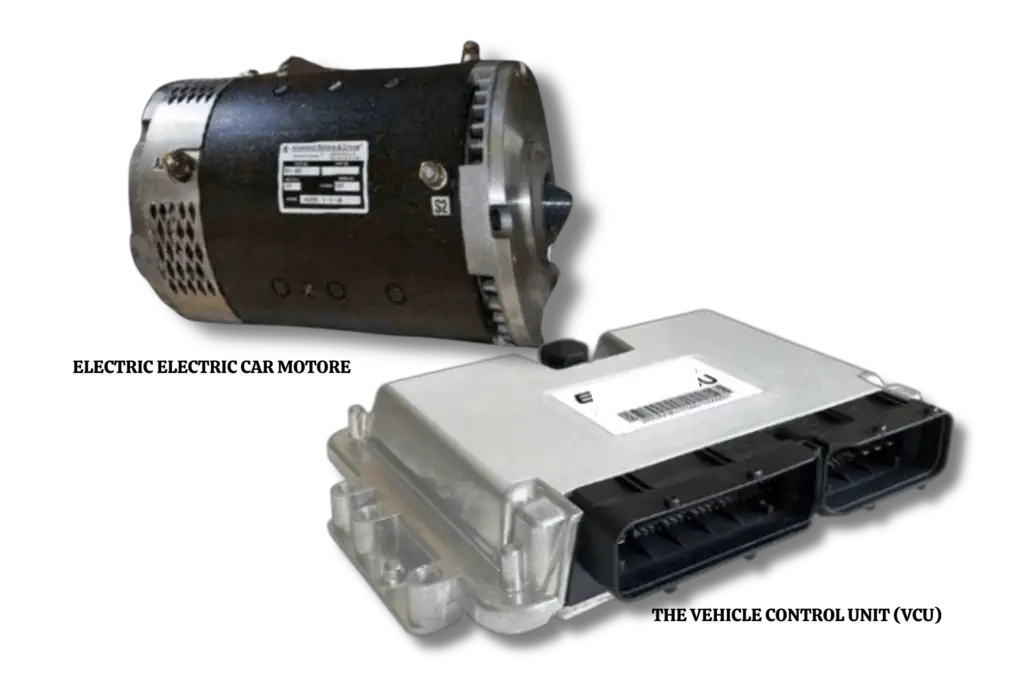

The brain of the automobile is the vehicle control unit (VCU), which oversees and coordinates all of an electric vehicle’s electrical systems.
The vehicle’s central unit, or VCU, is a specialized computer that analyzes data from sensors, including the thermal management system, motor controller, and battery management system.
Controlling the regenerative braking system, electric motor, and other vital parts may maximize the performance and efficiency of the vehicle.
To give the driver real-time information regarding the vehicle’s state, range, and charging status, the VCU communicates with the car’s onboard display and other user interfaces. The complex control algorithms of the VCU can contribute to the battery’s and other essential components’ longevity extensions.
The VCU is a crucial component that allows electric cars to run safely and effectively. Ultimately, the VCU is a vital part of what makes operating electric cars dependable, effective, and practical.
In-car entertainment and communication system

The in-car entertainment and communication system is a crucial part of modern electric cars, providing drivers and passengers with various features and functions to enhance the driving experience.
Many multimedia and entertainment features, including touchscreen displays, satellite radio, and smartphone connectivity, are frequently included in these systems. They often have advanced communication functions like speech recognition, hands-free calling and messaging, and navigational aids.
The features and information available to drivers through these systems are meant to be intuitive and straightforward, allowing access to various capabilities without detracting from the driver’s primary duty of driving.
Electric vehicles’ safety and convenience are also increasing. Many car manufacturers incorporate advanced driver-aid functions into their in-car entertainment and communication systems, such as lane departure alerts and adaptive cruise control.
Conclusion
An electric vehicle’s parts work together to power and manage the car, making it a practical, environmentally friendly, and silent method of transportation.
The battery pack is the energy source for the electric motor and other essential components. The electric motor transforms this energy into mechanical energy, which drives the wheels and moves the car forward.
Although the power electronics, which comprise the DC-DC converter and onboard charger, aid in managing and regulating the flow of electricity throughout the vehicle, the regenerative braking system aids in energy recovery when braking.
To ensure safe and Useful operation in various climatic circumstances, the thermal management system assists in controlling the temperature of the battery and other components.